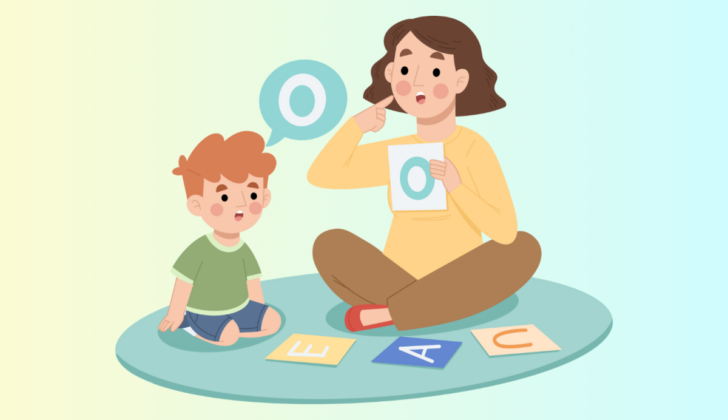
What is Speech?
Speech refers to the physical ability to produce sounds. It includes how we articulate words to express our thoughts and feelings. When we speak, we use our vocal cords, mouth, tongue, and lips. These are called our articulators. Good speech involves clear pronunciation, proper volume, and the ability to convey messages effectively.
For example, when a child says “dog,” they use their mouth and voice to make the sound. If a child struggles to say certain sounds or words, they may have a speech sound disorder. This can include the following:
Speech Sound Disorders:
- Articulation Disorders
-
-
-
- This is a problem with forming certain sounds. A person might say “wabbit” instead of “rabbit.”
-
-
- Phonological Disorders
-
-
-
- This is a type of speech sound disorder that involves difficulty with organizing speech sounds. This results in patterns of speech sound errors. For example, a person might have a pattern of leaving off the end sound of words (final consonant deletion) or replacing a sound that is made in the back of the mouth for a sound that is made in the front of the mouth (fronting).
-
-
- Childhood Apraxia of Speech
-
-
-
- This affects how children communicate. It makes it hard for them to say words correctly because their brains have trouble sending the right signals to the muscles used for speaking. The child knows what they want to say, their mouth may not move the way it should to make the sounds.
-
-
- Fluency Disorder
-
-
- Commonly known as stuttering. This is where a person repeats, prolongs, or blocks on sounds, words, and/or phrases.
-
- Voice Disorder
-
- This is a problem that affects how we speak and sound. A person’s voice might be hoarse, weak, or hard to hear.
What is Language?
Language, on the other hand, is broader and refers to the system of words and rules we use to communicate. It includes the words we choose and how we combine them to form sentences. Language can be spoken, written, or signed.
For example, when a child uses words to tell a story or ask a question, they are using language. Language involves grammar, vocabulary, and the ability to understand and express ideas. Children may face language difficulties if they struggle to express themselves or understand what others say.
Key Differences
- Components: Speech involves the physical sounds of communication, while language includes the meaning of those sounds and how we use them.
- Skills: Speech requires motor skills to produce sounds, while language involves cognitive skills to understand and use words.
- Disorders: Speech disorders affect how sounds are made, while language disorders affect understanding and using words correctly.
Why This Matters
Understanding the difference between speech and language is important for helping children communicate effectively. Parents and caregivers can play a vital role by encouraging both skills. Here are some tips:
- Encourage Speech: Play games that involve sounds, like rhyming or repeating tongue twisters. Singing songs can also help improve speech clarity.
- Support Language Development: Read books together and ask questions about the story. Encourage children to express their thoughts and feelings using complete sentences.
- Popular baby books to support language development.
- Popular toddler books to support language development.
- Popular preschool books to support language development.
- Popular school aged books to support language development.
- Be Patient: Children develop speech and language skills at different rates. It is essential to be patient and provide a supportive environment.
In summary, speech and language are two essential parts of communication. By understanding their differences, parents and caregivers can better support children as they grow and learn to express themselves. Encouraging both speech and language skills will help children become confident communicators!
Resources
For more information check out these resources