Understanding Warts
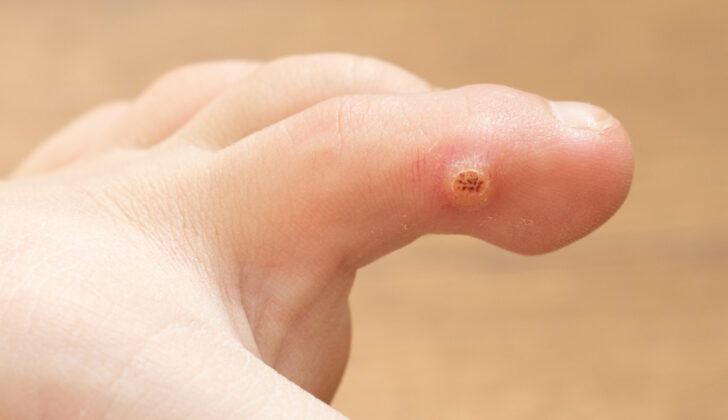
Warts are small, rough growths on the skin caused by a viral infection. They can show up on various parts of the body, most commonly on the hands, feet, and face. While generally harmless, warts can be unsightly and occasionally uncomfortable.
The Cause: Human Papillomavirus (HPV)
The primary cause of warts is the Human Papillomavirus (HPV). There are over 100 different types of HPV, each affecting different parts of the body. Here’s how HPV causes warts:
- Virus Entry: The virus enters the body through tiny cuts or breaks in the skin.
- Infection: Once inside, HPV infects skin cells and causes them to grow and form a wart.
- Spread: Warts can spread from one part of the body to another and from person to person through direct contact or sharing personal items like towels or razors.
Types of Warts
There are several types of warts, each with unique characteristics:
- Common Warts: Often found on the hands and knees, these warts have a rough surface and a dome-shaped appearance.
- Plantar Warts: These grow on the soles of the feet and can be painful due to the pressure of walking. They may have black dots in the center, which are tiny blood vessels.
- Flat Warts: These are smaller, smoother, and flatter than other warts. They often appear on the face, neck, and legs.
- Filiform Warts: These look like small, skin-colored tags or projections and usually appear on the face, especially around the mouth, eyes, and nose.
- Periungual Warts: These occur around the nails and can affect nail growth.
Risk Factors
Certain factors can increase the likelihood of developing warts:
- Age: Children and teenagers are more prone to warts because their immune systems are not fully developed.
- Skin Condition: People with cuts, scrapes, or a weakened immune system are at higher risk.
- Direct Contact: Touching warts on yourself or others, or using shared personal items, can spread the virus.
Prevention Tips
Preventing warts involves reducing the risk of HPV infection. Here are some tips:
- Avoid Direct Contact: Don’t touch warts on yourself or others. Use gloves or bandages if necessary.
- Keep Skin Clean and Dry: Moist environments can encourage the growth of warts.
- Don’t Share Personal Items: Avoid sharing towels, razors, socks, or shoes.
- Protect Your Feet: Wear flip-flops or sandals in public showers, locker rooms, and pool areas.
- Boost Your Immune System: A healthy diet, regular exercise, and adequate sleep can help keep your immune system strong.
Treatment Options
While many warts disappear on their own, some may require treatment, especially if they are painful, bothersome, or spreading. Common treatments include:
- Over-the-Counter Medications: These often contain salicylic acid, which helps to peel away the infected skin.
- Cryotherapy: This involves freezing the wart with liquid nitrogen.
- Prescription Treatments: A doctor may prescribe stronger medications or treatments, such as topical creams or injections.
- Surgical Removal: In severe cases, a doctor might remove the wart using minor surgery, laser therapy, or other methods.
When to See a Doctor
It is essential to see a healthcare provider if:
- The wart is painful or changes in appearance.
- You have warts on your face or genitals.
- The wart is not responding to over-the-counter treatments.
- You have a weakened immune system.
Conclusion
Warts, caused by the HPV virus, are common skin growths that can be prevented with good hygiene and care. While they are usually harmless, persistent or bothersome warts can be treated effectively. If you have concerns about a wart, consulting with a healthcare provider is always a good idea.